INFLUENCE OF NUTRIENTS ON EXTRATROPICAL SHALLOW WATER CARBONATES
 As part of an interdisciplinary international research effort, the complex interplay of
nutrients and other oceanographic controls on modern shallow water carbonate
depositional systems was quantified. We combined long-term field monitoring of
oceanography with sedimentologic and biologic investigations in a range of modern
carbonate environments distributed along a latitudinal gradient in the natural field
laboratory of the Gulf of California, Mexico. We were able to quantify for the first time the
influence of both temperature and nutrients on the development of modern shallow water
carbonates in a wide spectrum of environmental conditions. Data generated in the Gulf of
California can now be used to more accurately interpret or reinterpret paleoclimates and
paleoceanography from a large number of fossil carbonate systems worldwide.
As part of an interdisciplinary international research effort, the complex interplay of
nutrients and other oceanographic controls on modern shallow water carbonate
depositional systems was quantified. We combined long-term field monitoring of
oceanography with sedimentologic and biologic investigations in a range of modern
carbonate environments distributed along a latitudinal gradient in the natural field
laboratory of the Gulf of California, Mexico. We were able to quantify for the first time the
influence of both temperature and nutrients on the development of modern shallow water
carbonates in a wide spectrum of environmental conditions. Data generated in the Gulf of
California can now be used to more accurately interpret or reinterpret paleoclimates and
paleoceanography from a large number of fossil carbonate systems worldwide.
 |
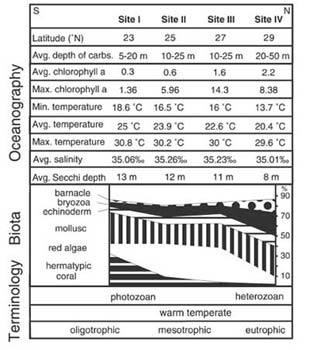 |
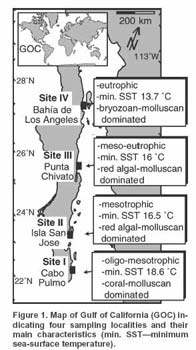
| Location map of Gulf of California, Mexico, indicating four study sites. In addition, lowest monthly winter seawater temperature isotherms at 10 m, average nutrient levels, and 200-m bathymetry contour are indicated. | Variations of oceanographic parameters and carbonate-producing biota across latitudes in Gulf of California. |
 |
| Compilation of types of modern shallow-water (<50 m) carbonate environments worldwide and respective temperature and chlorophyll a settings. Three associations can be distinguished. A photozoan association consists mainly of carbonate producers that require light for growth, and it forms at high temperatures and low nutrients (chlorophyll a being an indicator of nutrients). A heterozoan association is comprised of organisms that don’t need light for growth, and is usually found in low-temperature oceans .A heterozoan-photozoan transition zone is defined as forming at relatively high-temperatures and high nutrients. Study sites in the Gulf of California are indicated in the figure. |


ABOVE LEFT: Installation of oceanographic monitoring equipment in the Gulf of California
ABOVE RIGHT: Recovery of bottom sediment in the Gulf of California
ABOVE RIGHT: Recovery of bottom sediment in the Gulf of California